Number of Provinces - Union Find in C++ and Java
Problem Statement:
There are n cities. Some of them are connected, while some are not. If city a is connected directly with city b, and city b is connected directly with city c, then city a is connected indirectly with city c.
A province is a group of directly or indirectly connected cities and no other cities outside of the group.
You are given an n x n matrix isConnected where isConnected[i][j] = 1 if the ith city and the jth city are directly connected, and isConnected[i][j] = 0 otherwise.
Return the total number of provinces.
Example 1:
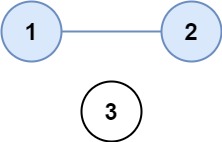
Input: isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 2
Example 2:
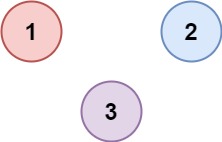
Input: isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 3
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j]is1or0.isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
Solution:
C++ solution:
class UnionFind
{
vector<int> roots;
vector<int> ranks;
public:
UnionFind(int sz)
{
roots = vector<int>(sz);
ranks = vector<int>(sz);
for(int i=0; i<sz; i++){roots[i]=i; ranks[i]=1;}
}
void unionSet(int x, int y)
{
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if (rootX==rootY) return;
if (ranks[rootX]==ranks[rootY]) ranks[rootX]++;
if (ranks[rootX]<ranks[rootY]) swap(rootX,rootY);
roots[rootY] = rootX;
}
int find(int x)
{
if (x==roots[x]) return x;
return roots[x] = find(roots[x]);
}
int numGroups(int sz)
{
unordered_set<int> mySet;
for (int i=0; i<sz; i++) mySet.insert(find(i));
return mySet.size();
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected)
{
int n = isConnected.size();
UnionFind uf = UnionFind(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)if(isConnected[i][j])
uf.unionSet(i,j);
return uf.numGroups(n);
}
};
Java solution:
class UnionFind
{
int[] roots;
int[] ranks;
public UnionFind(int sz)
{
roots = new int[sz];
ranks = new int[sz];
for(int i=0; i<sz; i++){roots[i]=i; ranks[i]=0;}
}
public int unionSet(int x, int y)
{
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if (rootX==rootY) return 0;
if (ranks[rootX]==ranks[rootY]) ranks[rootX]++;
if (ranks[rootX]< ranks[rootY])
{int temp=rootX; rootX=rootY; rootY=temp;}
roots[rootY] = rootX;
return 1;
}
public int find(int x)
{
if (x==roots[x]) return x;
return roots[x] = find(roots[x]);
}
public int numGroups(int sz)
{
HashSet<Integer> mySet = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i=0; i<sz; i++) mySet.add(find(i));
return mySet.size();
}
}
class Solution
{
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected)
{
int n=isConnected.length;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++)if(isConnected[i][j]==1)
uf.unionSet(i,j);
return uf.numGroups(n);
}
}