Count the Number of Complete Components - DFS + BFS + DSU solutions
Problem Statement:
You are given an integer n. There is an undirected graph with n vertices, numbered from 0 to n - 1. You are given a 2D integer array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] denotes that there exists an undirected edge connecting vertices ai and bi.
Return the number of complete connected components of the graph.
A connected component is a subgraph of a graph in which there exists a path between any two vertices, and no vertex of the subgraph shares an edge with a vertex outside of the subgraph.
A connected component is said to be complete if there exists an edge between every pair of its vertices.
Example 1:
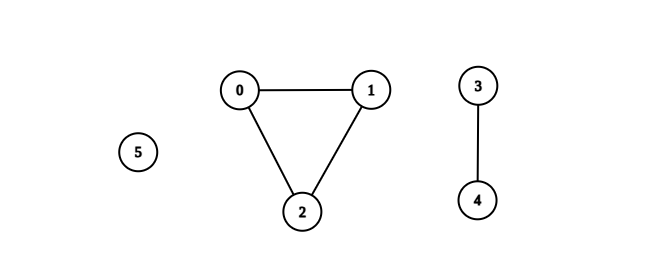
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2],[3,4]] Output: 3 Explanation: From the picture above, one can see that all of the components of this graph are complete.
Example 2:
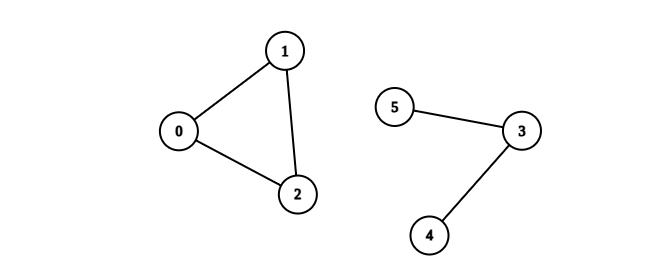
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2],[3,4],[3,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: The component containing vertices 0, 1, and 2 is complete since there is an edge between every pair of two vertices. On the other hand, the component containing vertices 3, 4, and 5 is not complete since there is no edge between vertices 4 and 5. Thus, the number of complete components in this graph is 1.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 500 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi <= n - 1ai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
Solution:
In any solution, all we need to do is count the number of nodes and edges in each connected component and increment answer every time $E = \frac12 * V * (V-1) $ where $E$ is the number of edges and $V$ is the nubmber of vertices in the connected component. Here I am providing DFS, BFS and DSU implmentations. In DSU implementation, I am using DSU with union by rank and path compression method which is the fastest in my experience. Read more about it here.
DSU solution:
class UnionFind
{
vector<int> roots, ranks, edges;
public:
UnionFind(int sz): roots(sz),ranks(sz),edges(sz)
{
for(int i=0; i<sz; i++)
{
roots[i]=i;
ranks[i]=0;
edges[i]=0;
}
}
void unionSet(int x, int y)
{
int rootX=find(x);
int rootY=find(y);
edges[rootX]++;
if (rootX==rootY) return;
if (ranks[rootX]==ranks[rootY])ranks[rootX]++;
if (ranks[rootX] <ranks[rootY]) swap(rootX,rootY);
roots[rootY] = rootX;
edges[rootX] += edges[rootY];
}
int find(int x)
{
if (x==roots[x]) return x;
return roots[x] = find(roots[x]);
}
int getAnswer()
{
int res=0;
unordered_map<int,int>H;
for(int i=0; i<roots.size(); i++) H[find(i)]++;
for (auto &[root, numNodes]: H)
{
int numEdges = edges[root];
if (numEdges == numNodes*(numNodes-1)/2) res++;
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int countCompleteComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges)
{
UnionFind uf = UnionFind(n);
for(auto &edge: edges)
{
int u=edge[0], v=edge[1];
uf.unionSet(u,v);
}
return uf.getAnswer();
}
};
DFS solution:
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>&G, int u, unordered_set<int>&component, int &ctr)
{
component.insert(u);
ctr += G[u].size();
for (int v: G[u]) if (!component.count(v)) dfs(G, v, component, ctr);
}
int countCompleteComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<vector<int>> G(n);
for(auto &edge: edges)
{
int u=edge[0], v=edge[1];
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
unordered_set<int> visited, component;
int ctr=0, res=0;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if (visited.count(i)) continue;
dfs(G, i, component, ctr);
ctr/=2; int nc=component.size();
if (ctr==nc*(nc-1)/2) res++;
visited.insert(component.begin(),component.end());
component.clear(); ctr=0;
}
return res;
}
};
BFS solution:
class Solution {
public:
int countCompleteComponents(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges)
{
vector<vector<int>> G(n);
for (auto &edge: edges)
{
int u=edge[0], v=edge[1];
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
queue<int> Q;
vector<int> visited(n,false);
int res = 0;
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if (visited[i]) continue;
int nodeCtr=0, edgeCtr=0;
visited[i] = true;
Q.push(i);
nodeCtr++;
while(!Q.empty())
{
for (int j=Q.size(); j>0; j--)
{
int cur = Q.front();
Q.pop();
edgeCtr += G[cur].size();
for (int nbd: G[cur]) if (!visited[nbd])
{
visited[nbd] = true;
Q.push(nbd);
nodeCtr++;
}
}
}
if (edgeCtr/2==(nodeCtr-1)*nodeCtr/2) res++;
}
return res;
}
};
In DFS and BFS, we put (edgeCtr/2) because we are counting each edge twice.