Binary Search Tree Iterator - Two solutions: Easy and Medium
Problem Statement:
Implement the BSTIterator class that represents an iterator over the in-order traversal of a binary search tree (BST):
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)Initializes an object of theBSTIteratorclass. Therootof the BST is given as part of the constructor. The pointer should be initialized to a non-existent number smaller than any element in the BST.boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there exists a number in the traversal to the right of the pointer, otherwise returnsfalse.int next()Moves the pointer to the right, then returns the number at the pointer.
Notice that by initializing the pointer to a non-existent smallest number, the first call to next() will return the smallest element in the BST.
You may assume that next() calls will always be valid. That is, there will be at least a next number in the in-order traversal when next() is called.
Example 1:
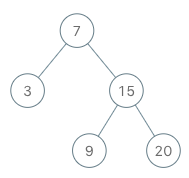
Input ["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"] [[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []] Output [null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false] Explanation BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]); bSTIterator.next(); // return 3 bSTIterator.next(); // return 7 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True bSTIterator.next(); // return 9 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True bSTIterator.next(); // return 15 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True bSTIterator.next(); // return 20 bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return False
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 106- At most
105calls will be made tohasNext, andnext.
Follow up:
- Could you implement
next()andhasNext()to run in averageO(1)time and useO(h)memory, wherehis the height of the tree?
Solution:
Easy Solution
Just traverse the array and store keys in an array. Then return answer from array.
class BSTIterator {
public:
vector<int>keys;
int idx;
void traverse(TreeNode *root, vector<int>&keys_v)
{
if (root==NULL) return;
traverse(root->left, keys_v);
keys_v.push_back(root->val);
traverse(root->right, keys_v);
}
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
traverse(root, keys);
idx=0;
}
int next() {
return keys[idx++];
}
bool hasNext() {
return idx < keys.size();
}
};
TC: O(1)
SC: O(n)
Medium Solution
Use stack to go as left as possible accumulating the nodes. Then return from bottom left and move to right (Accumulate nodes from right node to left-wards).
class BSTIterator {
public:
stack<TreeNode *>nodes;
void pushLeft(TreeNode *root)
{
while (root!=NULL)
{
nodes.push(root);
root=root->left;
}
}
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
pushLeft(root);
}
int next() {
if (nodes.size()>0)
{
TreeNode *leftBottom = nodes.top();
nodes.pop();
pushLeft(leftBottom->right);
return leftBottom->val;
}
else return -1;
}
bool hasNext() {
return nodes.size()>0;
}
};
TC: \u03B8(1)
SC: O(h)