Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row - BFS and DFS solutions
Problem Statement:
Given the root of a binary tree, return an array of the largest value in each row of the tree (0-indexed).
Example 1:
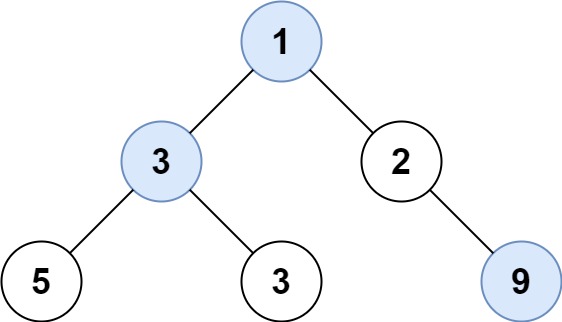
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] Output: [1,3,9]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3] Output: [1,3]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[0, 104]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Solution:
BFS in C++:
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root)
{
if (!root) return {};
queue<TreeNode*> Q;
Q.push(root);
vector<int> res;
while(!Q.empty())
{
int val = INT_MIN;
for(int i=Q.size(); i>0; i--)
{
TreeNode *cur = Q.front();
Q.pop();
if (cur->left) Q.push(cur->left);
if (cur->right) Q.push(cur->right);
val = max(val, cur->val);
}
res.push_back(val);
}
return res;
}
};
BFS in Java:
class Solution
{
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root)
{
if (root==null) return new ArrayList();
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList();
Queue<TreeNode> Q = new LinkedList();
Q.add(root);
while(!Q.isEmpty())
{
int val = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i=Q.size(); i>0; i--)
{
TreeNode cur = Q.poll();
if (cur.left!=null) Q.add(cur.left);
if (cur.right!=null) Q.add(cur.right);
val = Math.max(val, cur.val);
}
res.add(val);
}
return res;
}
}
DFS in C++:
class Solution
{
public:
void dfs(TreeNode *root, vector<int>&res, int d)
{
if (!root) return;
if (d==res.size()) res.push_back(root->val);
res[d] = max(res[d], root->val);
dfs(root->left, res, d+1);
dfs(root->right, res, d+1);
}
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root)
{
if (!root) return {};
vector<int> res;
dfs(root, res, 0);
return res;
}
};
DFS in Java:
class Solution
{
List<Integer> res;
void dfs(TreeNode root, int d)
{
if (root==null) return;
if (res.size()==d) res.add(root.val);
res.set(d, Math.max(res.get(d), root.val));
if (root.left!=null) dfs(root.left, d+1);
if (root.right!=null) dfs(root.right, d+1);
}
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root)
{
res = new ArrayList();
dfs(root, 0);
return res;
}
}