Max Area of Island - DFS solution
Problem Statement:
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid. An island is a group of 1's (representing land) connected 4-directionally (horizontal or vertical.) You may assume all four edges of the grid are surrounded by water.
The area of an island is the number of cells with a value 1 in the island.
Return the maximum area of an island in grid. If there is no island, return 0.
Example 1:
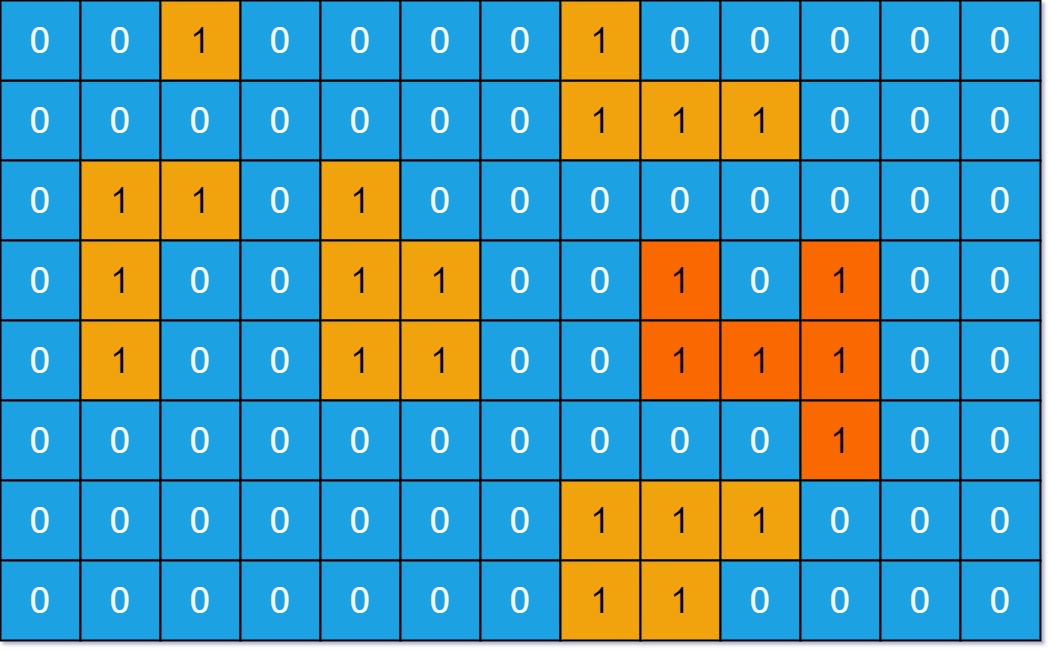
Input: grid = [[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]] Output: 6 Explanation: The answer is not 11, because the island must be connected 4-directionally.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]] Output: 0
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 50grid[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution:
class Solution {
public:
int util(int r, int c, vector<vector<int>> &grid, int m, int n, unordered_set<int> &visited)
{
if (r<0 || r>=m || c<0 || c>=n) return 0;
if (visited.count(n*r+c)>0 || grid[r][c]==0) return 0;
visited.insert(n*r+c);
return 1 + util(r-1,c,grid,m,n,visited) + util(r+1,c,grid,m,n,visited) + \
util(r,c-1,grid,m,n,visited) + util(r,c+1,grid,m,n,visited);
}
int maxAreaOfIsland(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m=grid.size(), n=grid[0].size(), res=0;
unordered_set<int> visited;
for (int r=0; r<m; r++)
for (int c=0; c<n; c++)
res = max(res, util(r,c,grid,m,n,visited));
return res;
}
};
class Solution:
def maxAreaOfIsland(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
seen = set()
def util(r,c):
if r<0 or r>=m or c<0 or c>=n or (r,c) in seen or grid[r][c]==0:
return 0
seen.add((r,c))
return 1+util(r+1,c)+util(r-1,c)+util(r,c+1)+util(r,c-1)
return max([max([util(r,c) for c in range(n)]) for r in range(m)])